Hydist
Simulating Riverbank Erosion with GPU
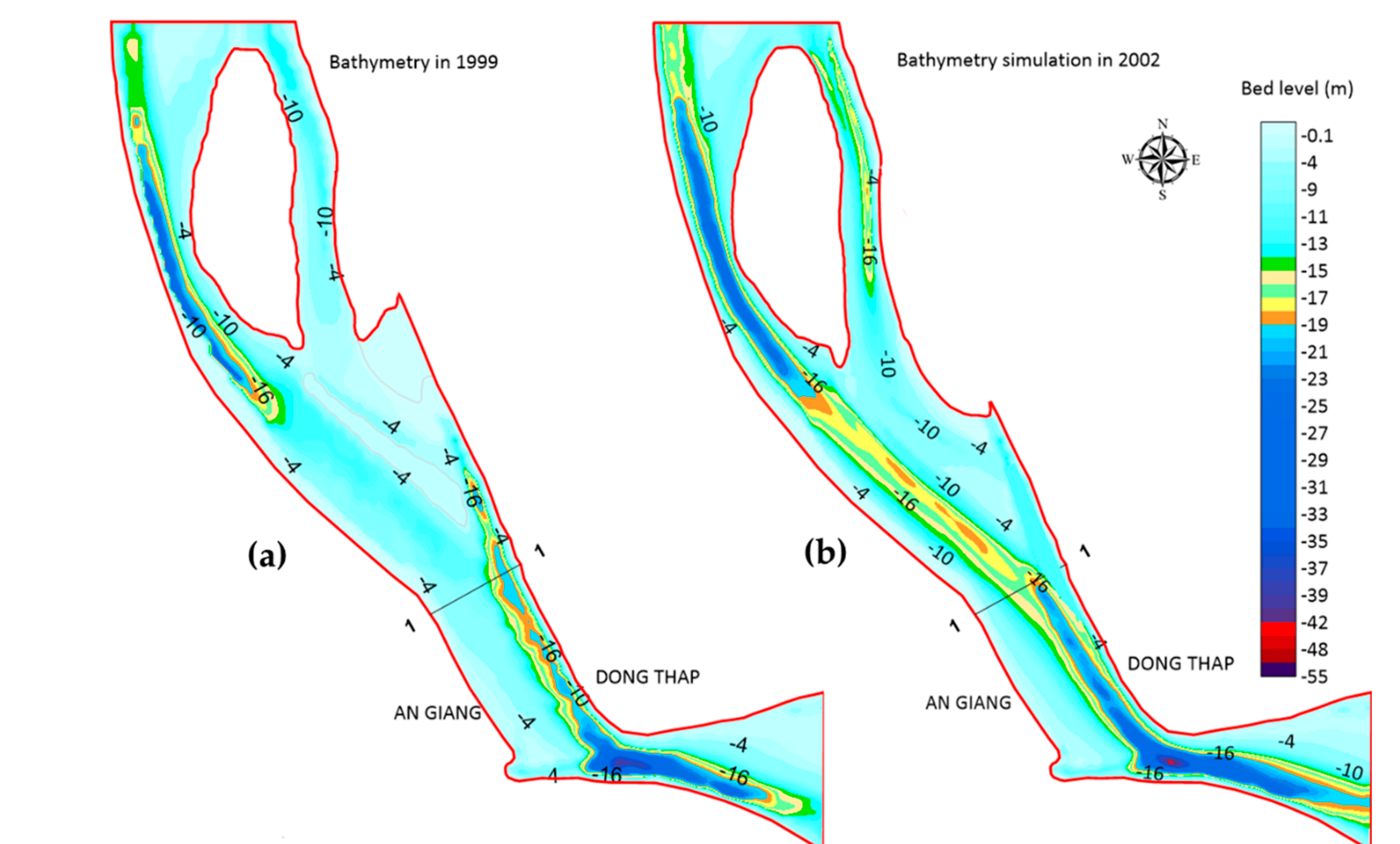
Riverbank erosion poses a significant threat to the lives of thousands of people residing along the riverbanks. By accurately predicting the occurrence of erosion and understanding the impact of activities like sand mining on riverbanks, we can save countless lives. Riverbank erosion simulation can inform authorities to take prompt action and implement regulations to safeguard the riverbanks. However, simulating the impact of human activities on riverbanks requires extensive computational resources, hindering research progress.
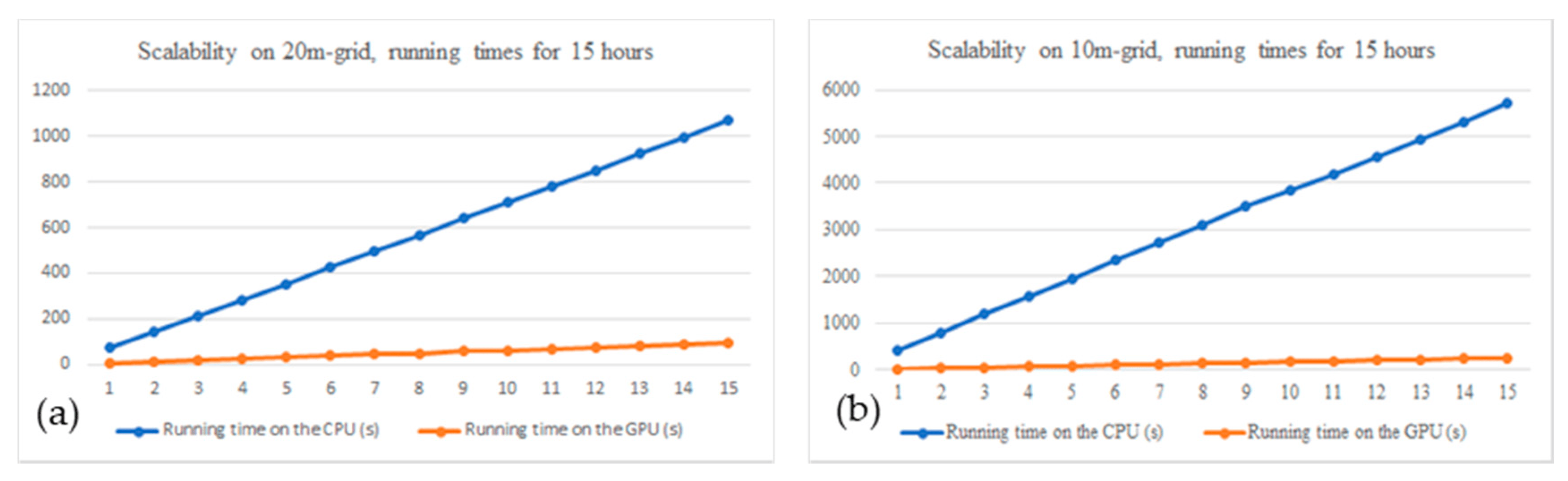
In this project, we attempted to solve this computational bottleneck by building a simulation system on GPUs. Our system accurately simulated changes in river flow and riverbeds, providing information to predict riverbank erosion while running orders of magnitude faster than traditional simulation systems that run on CPUs. This project is a collaborative effort from researchers at UNIST, South Korea, and Vietnam National University, HCM.
Role:
- Collaborateed with hydrologist scientist to create numerical solvers to Shallow-Water-Equations, Sediment-Transfort-Equation
- Implemented these solvers in python and validate the accuracy
- Implemented these solvers in CUDA and validate the accuracy
- Optimized the performance of the CUDA code on NVIDIA Titan-X GPU
Publication:
Thi Kim, Tran, Nguyen Thi Mai Huong, Nguyen Dam Quoc Huy, Pham Anh Tai, Sumin Hong, Tran Minh Quan, Nguyen Thi Bay, Won-Ki Jeong, and Nguyen Ky Phung. 2020. “Assessment of the Impact of Sand Mining on Bottom Morphology in the Mekong River in An Giang Province, Vietnam, Using a Hydro-Morphological Model with GPU Computing” Water 12, no. 10: 2912. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102912